Postoperative Oral Antibiotics and Sinonasal Outcomes Following Endoscopic Transsphenoidal Surgery for Pituitary Tumors (POET) Study
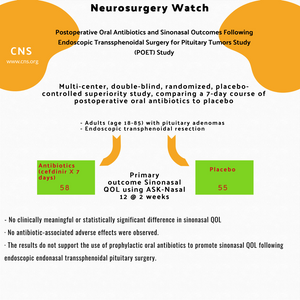
- Inclusions: Adults (age 18-85) with pituitary adenomas (non-functioning, acromegaly or prolactinoma) having undergone binostril endoscopic endonasal pituitary surgery
- Exclusions: Patients with Cushing, and those for whom nasoseptal flap was planned.
- Primary outcomes: Sinonasal quality of life (QOL) using Anterior Skull Base Nasal Inventory 12 (ASK-Nasal 12) at 2 weeks.
- Secondary outcomes: Sinonasal QOL using Sinonasal Outcome Test-22 (SNOT-22), and objective endoscopy scores to assess nasal healing using the Lund-Kennedy method.
- Results: 113 patients analyzed: 55 placebo group, 58 antibiotic group. Antibiotic group received cefdinir for 7 days.
- There was no clinically meaningful or statistically significant difference in sinonasal QOL at any of the reported time-points using either patient-reported QOL instrument (p≥0.24).
- Nasal cavity endoscopy scores were not statistically significantly different at 1-2 weeks, or 3-4 weeks post-operative.
- Most patients returned to baseline sinonasal QOL scores by 8 weeks post-operative.
- Four patients in the antibiotic group and 7 patients in the placebo group were diagnosed with sinusitis (p=0.35).
- No antibiotic-associated adverse effects were observed.
- Conclusion: These results do not support the use of prophylactic oral antibiotics to promote sinonasal QOL following endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal pituitary surgery.
Little et al. NEUROSURGERY, 2021.
This summary was published in Oct. 21.
Source
Source:
NEUROSURGERY